- Superior HVAC Service
- 416-259-6767
- 905-470-7555
- Alliance.Markham@gmail.com
5 Main Components Of An Air Conditioner & Their Role
How Often Should Your HVAC Systems Be Serviced?
September 22, 20215 Signs It’s Time To Replace Your Old Hvac System
September 24, 20215 Main Components Of An Air Conditioner & Their Role
An air conditioner system may be a matter of comfort or necessity in many homes today, but it was once a luxury. Having an hvac at home will give you peace of mind knowing that you can withstand even the hottest summer thanks to the cooling effect of this system. It is fascinating to note what an air conditioner system can do for a home or a workspace.
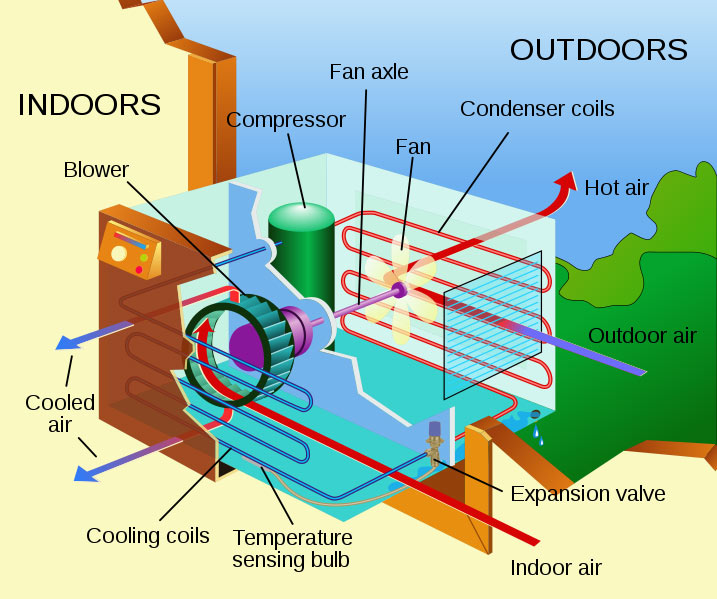
Several components make up an air conditioner system and each performs a specific task needed for the system to operate optimally. An understanding of these components and the role they play will help you get a better idea of how an air conditioner works.
Here are 5 main components of an air conditioner and the role they play in cooling your home.
Compressor
This is your air conditioner’s engine. It is responsible for turning gas into liquid. The compressor of your air conditioner transforms the low pressure refrigerant into a high pressure gas that has high temperature. Energized gas is created by narrowing down the gaps between molecules. This then enters the condenser. This unit is what helps to cool down the warm air and creates the cooling effect desired.
Condenser coil
The condenser coil is fitted to a fan. The role of this component is to cool down the high pressure gas coming from the compressor and convert it into a liquid form. Both the compressor and the condenser coil of your air conditioner system will typically be located outside the house. The liquid produced is then carried to the next important component of your air conditioner: the evaporator.
Evaporator
This component is located inside the home. A thin pipe links the condenser coil with the evaporator. The low pressure liquid from the condenser coil reaches this component. The pressure here is extremely low and converts the liquid back into gas. The heat from the air is removed and it cools off in a cyclic manner.
Air handler and blowing unit
These two units play a crucial role in drawing warm air into the AC system and blowing cool air out into rooms of the house. They help with the equal distribution of cold air throughout the room.
Thermostat
The thermostat allows you to control the temperature of your air conditioner and regulate the amount of heat energy that flows into the unit and out from the unit. This can be adjusted manually or automatically based on the type of thermostat you have.